Nutritional value
As we now know, veal is still considered a luxury product in northern Europe and is mainly eaten in restaurants. In the south of Europe, it is still the women doing the food shopping on Saturdays and they are more than happy to buy veal on a regular basis. In these countries, veal is seen as a delicacy, but one that works well as part of a healthy and nutritional diet. It is a responsible choice, mainly because it is so easy to digest. Let’s have a look at the nutritional value of veal. For this analysis, we chose 100 g of entrecôte, raw. The energy value of veal is particularly low. If you consider that an average male needs to consume 2000 kcal per day, then he would have to eat an awful lot of veal! This energy value is almost the same as fish. Halibut, for example, has an energy value
| Energy | 176 kcal / 699 kJ |
| Fat | 6,3 g |
| Fibre | 0 |
| Water | 71 g |
| Protein | 27,5 g |
| Cholesterol | 60,5 mg |
| Carbohydrates | 0 |
The energy value of veal is particularly low. If you consider that an average male needs to consume 2000 kcal per day, then he would have to eat an awful lot of veal! This energy value is almost the same as fish. Halibut, for example, has an energy value of 143 cal/100 g.
| Vitamins | |
| A1 equivalents | 18 μg |
| B1 | 0,06 mg |
| B2 | 0,13 mg |
| B3 | 6,1 mg |
| B6 | 0,449 mg |
| B9 equivalents | 6,0 μg |
| B12 | 1,71 μg |
| D | 0,1 μg |
| E | 0,3 mg |
We need vitamin A for our skin and for preventing night blindness. We need B1, B2 and B9 for our metabolism and B3 for the citric acid cycle (Krebs Cycle). Vitamin B6 is important for muscle development, the formation of blood cells and our DNA. B12 is a co-enzyme that helps prevent anaemia, whilst vitamin D is important for our bones and teeth. Finally then, vitamin E, which is an important anti-oxidant.
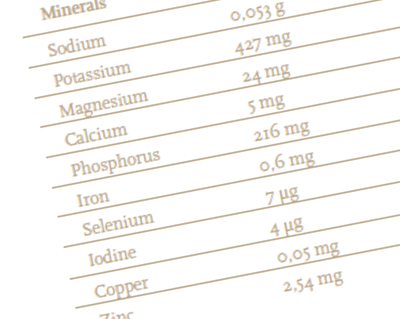
| Minerals | |
| Sodium | 0,053 g |
| Potassium | 427 mg |
| Magnesium | 24 mg |
| Calcium | 5 mg |
| Phosphorus | 216 mg |
| Iron | 0,6 mg |
| Selenium | 7 μg |
| Iodine | 4 μg |
| Copper | 0,05 mg |
| Zinc | 2,54 mg |
Sodium and potassium play an important role in our bodies in fluid retention, our nervous system and our muscles. Magnesium is important for our muscles, joints and metabolism and calcium and phosphorus for our bones and teeth. We need iron for a healthy metabolism and blood, whilst selenium helps improve our immune system and slows down the ageing process. Iodine helps us burn fat and copper is needed for healthy blood, bones, cartilage and skin pigments. Zinc works with our immune system to promote healing.